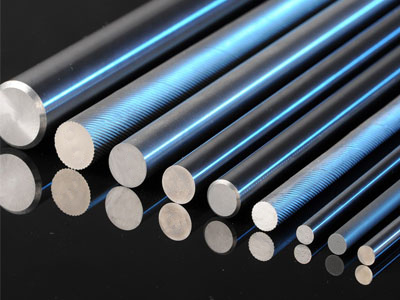
Carbide Rods With Single Hole
Carbide Rods with single hole
standard grades : BT10 and BT10X
Submicro Grain Size, with all HIP treatmemt
1. Tungsten Carbide rods with single hole are used to make tools for applications requiring internal through coolant.
2. These rods are also used to manufacture dampening or anti vibration boring bars and also tool holders of extra long lengths with internal through coolant supply. These rods are specially used for machining components with blind holes so that the coolant forces out chips from the bottom of the hole which otherwise cannot be done with external coolant supply.
3. Single hole rods are used for manufacturing mostly straight flute solid carbide tools like reamers, hole mills, Taps, bottoming drills etc.
One Central Coolant Duct Rods
Type: 1SH
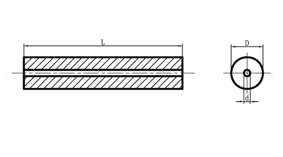
One Central Coolant Duct Rods Type: 1SH
| Unground |
Ground h6 |
d(mm) |
L +5.0mm |
a |
D mm |
Tol. |
4.3 |
0/+0.3 |
4 |
0.6-2.0 |
330 |
0.15 |
5.3 |
5 |
6.3 |
6 |
7.3 |
7 |
0.8-3.0 |
8.3 |
8 |
9.3 |
9 |
0.20 |
10.3 |
10 |
0.8-4.0 |
11.3 |
0/+0.4 |
11 |
12.3 |
12 |
13.3 |
13 |
0.8-6.0 |
0.30 |
14.3 |
14 |
15.3 |
15 |
16.3 |
16 |
17.3 |
0/+0.5 |
17 |
0.8-7.0 |
0.40 |
18.3 |
18 |
19.3 |
19 |
20.3 |
20 |
0.50 |
22.3 |
22 |
24.3 |
24 |
25.3 |
25 |
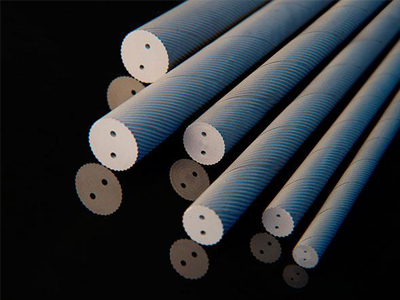
Carbide Rods with Two Parallel Holes
Reduced TK/Standard TK
Carbide rod with two holes
standard grades (Reduced TK): BT10X
standard grades (Standard TK): BT10
Submicro Grain Size, with all HIP treatmemt
1. Tungsten Carbide rods with Double holes are used to make tools for applications requiring internal through coolant supply.
2. These rods are also used to manufacturing dampening or anti vibration tool holders of extra long lengths with internal through coolant supply. These rods are specially used for machining components with blind holes so that the coolant forces out chips from the bottom of the hole which otherwise cannot be done with external coolant supply.
3. Double hole rods are used for manufacturing mostly straight flute solid carbide tools like reamers, hole mills, bottoming drills etc.
Two Parallel Coolant Ducts Rods Type: 2SH
| Unground |
Ground h6 |
mm |
Tol. |
d(mm) |
Tol. |
L +5.0mm |
a mm |
| D mm |
Tol. |
| 6.3 |
0/+0.3 |
6 |
1.50 |
0/-0.20 |
0.80 |
±0.15 |
330 |
0.15 |
| 7.3 |
7 |
1.50 |
0.80 |
0.15 |
| 8.3 |
8 |
2.60 |
0/-0.30 |
1.00 |
0.15 |
| 9.3 |
9 |
2.60 |
1.00 |
0.20 |
| 10.3 |
10 |
2.60 |
1.00 |
0.20 |
| 11.3 |
0/+ 0.4 |
11 |
3.50 |
1.20 |
0.28 |
| 12.3 |
12 |
3.50 |
1.20 |
0.30 |
| 13.3 |
13 |
3.50 |
1.20 |
0.34 |
| 14.3 |
14 |
5.00 |
1.50 |
0.37 |
| 15.3 |
15 |
5.00 |
1.50 |
0.40 |
| 16.3 |
16 |
5.00 |
1.50 |
±0.20 |
0.40 |
| 17.3 |
0/+ 0.5 |
17 |
6.20 |
2.00 |
0.47 |
| 18.3 |
18 |
6.20 |
2.00 |
0.50 |
| 19.3 |
19 |
6.20 |
2.00 |
0.50 |
| 20.3 |
20 |
6.20 |
0/-0.40 |
2.00 |
±0.30 |
0.50 |
Two straight coolant duct
rods, Reduced TK

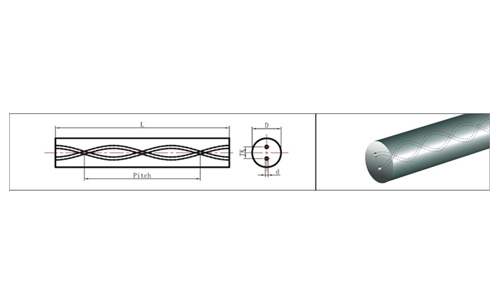
Threaded Carbide Rods with Two Helical Holes
(Type 2H-30°/40°)
Available Grades(Type 2H-30°):
BT10 / BT10X
Available Grades(Type 2H-40°):
BT10 /
BT10X
Submicro Grain Size, with all HIP treatmemt
1. Threaded carbide rods with Helical coolant holes are mainly used for manufacturing Helical fluted high performance drills.
2. Drills with Helical Coolant Holes can run at very high cutting parameters as the two or three Helical
coolant holes facilated high presure and flow of coolant.
3. Threaded Carbide rod with Helical coolant holes are used for making gun drill blanks, high performance drills for aluminum castels step drills and other various types of special tools.
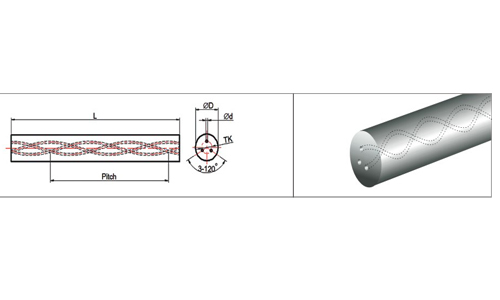
Threaded Carbide Rods with Three Helical Holes
(Type 3H-40˚)
Three Helical Coolant Duct :
Avaliable Grades : BT10 / BT10X
1. Threaded carbide rods with Helical coolant holes are mainly used for manufacturing Helical fluted high
performance drills.
2. Drills with Helical Coolant Holes can run at very high cutting parameters as the two or three Helical
coolant holes facilated high presure and flow of coolant.
3. Threaded Carbide rod with Helical coolant holes are used for making gun drill blanks, high performance
drills for aluminum castels step drills and other various types of special tools.
Two 30º Helical Coolant Ducts Rods Type 2H-30°
| Unground |
Ground h6 |
L Tol.0/ +5 |
HE-30° |
2H-30° |
Pitch |
| D |
Tol. |
TK |
Tol. |
d |
Tol. |
TK |
Tol. |
d |
Tol. |
| 4.3 |
+0.3 / +1.3 |
4.0 |
330 |
2.10 |
±0.1 |
0.60 |
±0.1 |
2.10 |
±0.1 |
0.60 |
±0.1 |
21.77 |
| 5.3 |
5.0 |
2.10 |
±0.2 |
0.70 |
|
±0.2 |
|
27.21 |
| 6.3 |
6.0 |
2.70 |
0.80 |
2.40 |
0.70 |
32.65 |
| 7.3 |
7.0 |
3.50 |
1.00 |
±0.15 |
|
|
±0.15 |
38.09 |
| 8.3 |
8.0 |
3.40 |
1.00 |
3.80 |
1.00 |
43.53 |
| 9.3 |
9.0 |
4.50 |
±0.3 |
1.40 |
|
±0.3 |
|
48.97 |
| 10.3 |
10.0 |
4.80 |
1.30 |
4.50 |
1.40 |
54.41 |
| 11.3 |
11.0 |
4.90 |
±0.4 |
1.40 |
|
±0.4 |
|
59.86 |
| 12.3 |
12.0 |
6.30 |
1.70 |
±0.20 |
5.85 |
1.40 |
±0.20 |
65.3 |
| 13.3 |
13.0 |
6.10 |
1.75 |
|
|
70.74 |
| 14.3 |
14.0 |
6.70 |
1.80 |
6.70 |
1.75 |
76.18 |
| 15.3 |
15.0 |
7.30 |
1.75 |
|
|
81.62 |
| 16.3 |
16.0 |
8.00 |
2.00 |
7.90 |
1.75 |
87.06 |
| 17.3 |
17.0 |
8.50 |
1.75 |
|
|
92.5 |
| 18.3 |
18.3 |
9.00 |
±0.45 |
2.30 |
9.15 |
2.00 |
±0.25 |
87.95 |
| 19.3 |
19.0 |
9.70 |
±0.4 |
2.00 |
±0.25 |
|
|
103.39 |
| 20.3 |
20.0 |
10.0 |
±0.5 |
2.50 |
±0.20 |
9.90 |
±0.5 |
2.00 |
108.83 |
Two 40º helical Coolant Ducts Rods Type 2H-40°
| Unground |
Ground h6 |
L Tol.0/ +5 |
TK |
Tol. |
d |
Tol. |
Pitch |
| D |
Tol. |
| 6.3 |
+0.3 / +1.3 |
6.0 |
330 |
1.90 |
±0.15 |
0.70 |
±0.10 |
22.46 |
| 8.3 |
8.0 |
2.40 |
0.65 |
±0.15 |
29.95 |
| 10.3 |
10.0 |
3.10 |
±0.30 |
0.80 |
37.44 |
| 12.3 |
12.0 |
3.80 |
±0.40 |
0.90 |
44.93 |
| 14.3 |
14.0 |
4.30 |
1.00 |
±0.20 |
52.42 |
| 16.3 |
16.0 |
5.10 |
1.20 |
59.90 |
| 18.3 |
18.0 |
5.90 |
1.40 |
67.39 |
| 20.3 |
20.0 |
6.60 |
±0.50 |
1.50 |
74.88 |
Three 30˚Helical coolant Ducts (Type 3HE-30˚)
| Unground |
Ground h6 |
L Tol.0/ +5 |
TK |
Tol. |
d |
Tol. |
Pitch |
| D |
Tol. |
| 6.3 |
+0.2 / +1.0 |
6.0 |
330 |
2.75 |
±0.20 |
0.50 |
±0.15 |
32.65 |
| 8.3 |
8.0 |
3.85 |
0.70 |
43.53 |
| 10.3 |
10.0 |
4.95 |
±0.30 |
0.85 |
±0.20 |
54.41 |
| 12.3 |
12.0 |
6.05 |
±0.40 |
1.10 |
65.30 |
| 14.3 |
14.0 |
7.05 |
1.40 |
76.18 |
| 16.3 |
16.0 |
8.05 |
1.60 |
87.06 |
| 18.3 |
18.0 |
9.25 |
±0.50 |
1.70 |
±0.25 |
97.95 |
| 20.3 |
20.0 |
9.85 |
1.90 |
108.83 |
Manufacturing Process of Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten Carbide, It should be referred as Cemented Carbide, is manufactured by powder
metallurgy methods. The tungsten carbide powders are mixed with
a binder metal, which is normally
cobalt or nickel in 3-28%, compacted in a die and then sintered in a furnace generally between
1350-1450︒C.
In additional to
the traditional sintered carbide, BTC is also able to offer the Pre-forming parts which
is suitable for complicate shapes or small batches which is hard to afford to
make a new die.
By our variety of forming routes, BTC is able to produce the tungsten carbide parts up to 500 mm in
length and up to 200 mm in diameter,
with minimum order quantity starts from 5 pc.
1. Grade Design
BTC grades are designed based on application requirements. Our process start with powder mixing.
Raw materials includes WC, Co and other elements.
2. RTP Ball milling
Wide variety of BTC designed grades from superfine to coarse grain size are available.
Grade with different grain size are ball-milled, sieved, granulated in
separated systems to avoid grain contamination.
3. Spray Drying
Spray drying process makes the powder into superior homogeneous particle
sizes with good flowability and as a result, the dimension variation on
sintered blank is minimum.
4.1. Extrusion
The rods with or without coolant holes, including Helical types, are formed by extrusion pressing.
Our automatic extrusion systems and technical know-how helps to achieve consistent dimentions and other properties.
4.2. Direct Pressing
Due to our comprehensive and variable forming solutions, we are able to produce
the various type of rods by extrusion pressing, and also the direct pressing of
blanks such as rotary burr blanks, disc cutters etc.
Special developed grades
based on applications, high precision press tools designed
built in house, offer tighter tolerance control,
which ensures higher performance of
products delivered to you.
5.1.Preforming
Turning, milling, drilling, cutting can be applied on green blanks ( half sintered condition ) in order
to preform the part to net shape according to customer's drawing, which can
greatly enhance customer's productivity for special and complicated tools.
5.2. Drying Process
This process removes the plasticizer in the blanks using a vacuum drying furnace.
6. Sintering
Green blanks (half sintered condition) are sintered at temperature around 1400℃ (cobalt melting)
to become super hard and tough.
BTC utilizes HIP (hot isostatic pressure) sintering
furnace which gives carbide maximum,
toughness to meet the most critical working applications.
7. Machining
Rod blanks need to be centerless ground,to achieve precision tolerance h6/h5.
In addition,
upon customer's request we offer length cutting, chamfer, slot, cylindrical grinding services etc..
8. Inspection
The key properties are monitored from raw material, RTP and raw sintered parts
in our laboratory for quality and performance guarantee.
Diameter, roundness,
run-out, roughness, pitch, TK, concentricity, inspection will be done before the parts
are shipped to the customer.